Background
For over 70 years, antibiotic susceptibility testing has been performed in laboratories worldwide. These tests involve measurement of a clear area that surrounds an antibiotic disk on an agar plate, known as the “zone of inhibition”. This zone indicates the bacteria’s sensitivity to the antibiotic. The basic principle of measuring zones of inhibition microbiology dates back to the 1930s when Alexander Flemming observed the inhibitory effect of Penicillium on bacteria that was growing on agar plates, thereby laying the groundwork for future antibiotic discovery.
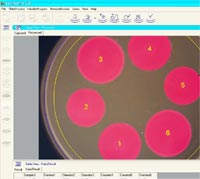
In the 1950s, the Kirby-Bauer method, a disk diffusion technique was established as the industry standard for antibiotic susceptibility testing. For this process, researchers inoculate specimen bacteria onto an agar plate, place the antibiotic disks on the plate’s surface, then measure the diameter of the inhibition zone to determine the bacteria’s susceptibility to the antibiotic.
There are two ways to perform this process, manually and by using devices specifically designed to facilitate this process, known as zone inhibition readers. Initially, every zone diameter was measured manually using calipers or standardized rulers. However, this process was not completely effective, as researchers could easily introduce zone measurement variability due to both user error and different batch interpretations.
It was not until the 1970s that the first automated zone inhibition reader was invented and patented. Today’s versions of this advancement in microbiology technology incorporate features such as digital calipers, automated image analysis, as well as software that both accurately measures and interprets each zone diameter, thereby vastly improving accuracy, consistency, and efficiency for microbiology laboratories. Zone inhibition readers devices are designed to perform exactly what their name states: they measure the zone of inhibition, which is the means by which microbiologists test the effectiveness of antibiotics on microorganisms. The zone of inhibition microbiology process, which was once widely considered to be one of the most time-consuming tasks requiring concentration to ensure accuracy, has been greatly improved through the continued development of zone inhibition readers.
Benefits of Using Zone Inhibition Readers in Microbiology Laboratories
Interpretive Software
Zone inhibition reader devices are integrated with software provided by their manufacturer to compare measured zone diameters against established clinical breakpoints. This process provides a direct and highly accurate interpretation of bacterial susceptibility, i.e. susceptible, intermediate or resistant results.
Calibration
To maintain the highest levels of accuracy in measurement, zone inhibition readers require regular calibration maintenance. This process is performed by a calibration professional using a calibrated reference standard of known uncertainty (as stated in the industry’s calibration traceability pyramid) to compare with a device under test. Readings are recorded from the device under test and compared to the readings from the reference source. This process ensures that future readings from the device will be accurate and effective.
Clinical Impacts
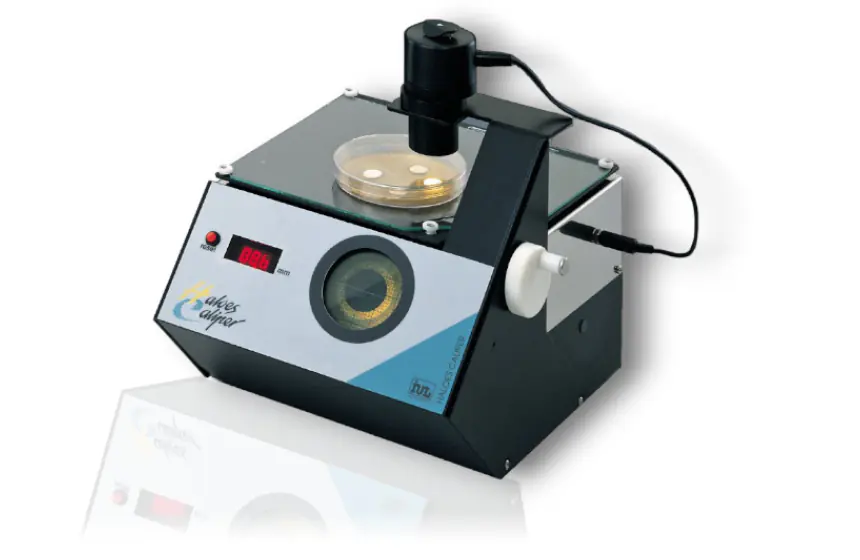
Understandably, accurate zone inhibition readings are critical to making appropriate antibiotic therapy decisions in clinical microbiology laboratories. That is why Neutec is proud to offer the Haloes Caliper Zone Reader. This device semi-automates the zone diameter measurements, providing for faster, far more accurate readings and outcomes than those produced by manual processes. The Haloes Caliper Zone Reader operates by allowing an enlarged image, semi-automated zone diameter measurement, thereby avoiding parallax errors in readings. The value of this laboratory equipment is speed, accuracy, and highly reproducible, quantitative results for all your zone inhibition antibiotic measurements.
Neutec also recommends purchasing the Haloes Caliper – Zone Inhibition Reader accessories which include the Grid, Mask of 4 Small Cups (10 Units), Mask of 6 Small Cups (10 Units) as well as Test Gauges all specifically designed for use with this model. Speak with Neutec’s knowledgeable representatives to learn which solution is best for your microbiology laboratories applications.