Since water activity testing is critical to ensure quality and safety of manufactured products, it is common to find water activity instruments in most quality assurance laboratories. As with any laboratory test method, good laboratory practices require routine verification assessments for water activity to make sure the instrumentation is working properly. This can be accomplished by running tests on standards of known value and comparing the test results to the actual values. While this can be difficult for some common quality assurance tests that do not have independent standards, such as moisture content, water activity standards exist in the form of electrolytic (salt) solutions. These water activity standards are one of the most important tools available to laboratory personnel to provide them with confidence in their water activity testing results and facilitate troubleshooting.
Introduction
A chance in results when testing salt standards indicates some change in the instrumentation that could be impacting the integrity of product test results. For instruments that rely on a chilled mirror sensor, changes in standard readings are typically the result of contamination of the mirror, which can happen at any time, making frequent verification with salt standards necessary. For instruments using electrolytic sensors, due to their resistance to problems from contamination, salt standards can be used less frequently and serve the purpose of determining if an instrument calibration is needed.
Verification With Standards
Water activity standards are used to verify water activity instruments by placing a standard in a testing cup and then placing the cup in the instrument. For some instruments, verification is performed like any other water activity test. Then the user compares the result to the actual value at the appropriate temperature and if the test result is within the instrument tolerance of the actual value, the instrument passes verification. If not, the instrument is inspected for cleanliness, or the calibration is adjusted until successful verification is achieved. With more advanced instruments such as the LabMaster NEO from Novasina, the process is automated. The instrument recognizes which standard is being used, knows the true value, determines if the verification passed, and if not, applies a calibration replacement.
Verification Standards
Salt standards that cover the full water activity range of 0 to 1.00 are available and typically 2 or more standards will be used for verification. The value of the standard will depend on the type of salt used, the temperature, and the type of the standard. Water activity standards are available in two types, saturated slurries, and unsaturated solutions.

Saturated Salt Slurries
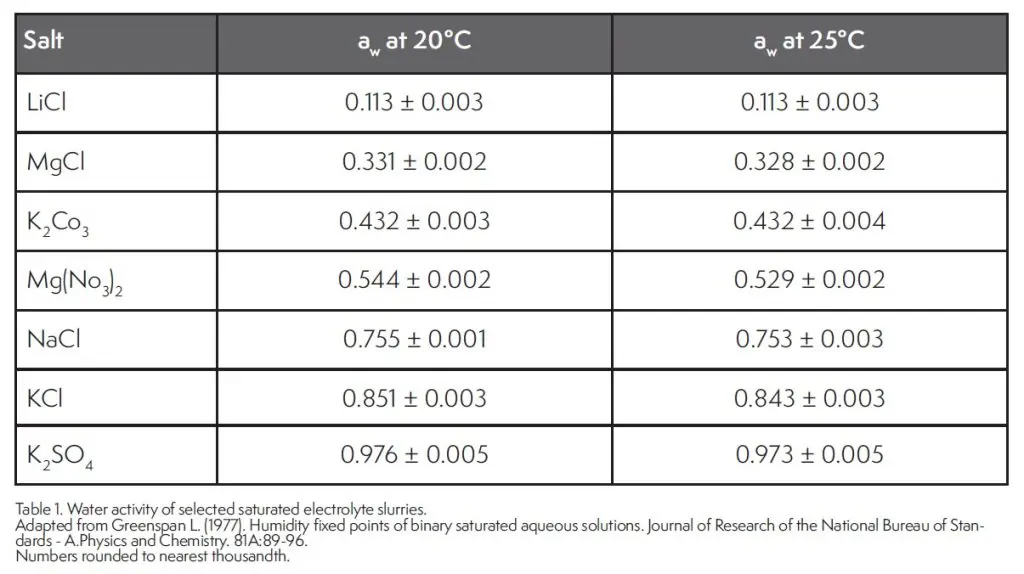
Independent water activity standards are made possible by the unique characteristics of crystalline electrolytes. These salts have well defined thermodynamic properties including that at saturation, the will remain a constant water activity if temperature remains constant. The water activity value of the saturated slurry depends on the type of salt and the temperature. Table 1 provides a short list of the water activity values of several saturated slurries and a more complete list is available from Greenspan (1977). A saturated slurry is prepared by starting with quantity of crystalline salt and then adding distilled water in small increments while stirring until the salt cannot absorb any more water as evidenced by it taking on the shape of the container, but not being easily poured (Fontana and Carter 2020).
Unsaturated Salt Solutions
In addition to saturated slurry standards, unsaturated salt solutions can also be used as water activity standards. For this type of standard, it appears as solution with no visible salt crystals as all the salt is solubilized. The water activity of an unsaturated salt solution is determined by both the salt and the solution concentration. The water activity of an unsaturated salt solution is calculated by equation (1):
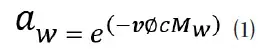
Where v is the number of dissociation ions for the salt, ø is the osmotic coefficient for the salt, c is the molal concentration, and Mw is the molecular mass of water (Robinson and Stokes 1965). Using this equation, it is possible to create a salt solution standard to any water activity value by solving molal concentration in equation (1).

Which Standard Is Best?
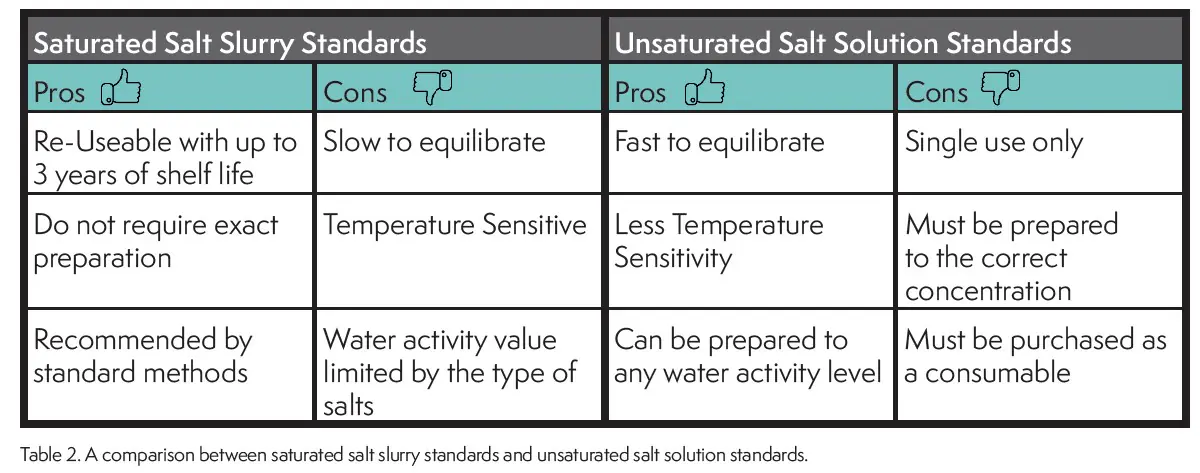
As would be expected both types of standards have advantages and disadvantages (Table 2). The advantage of saturated slurry standards is that they can be re-used indefinitely if maintained properly and are easily prepared without a precision balance and complicated recipes. Their disadvantages is that they take longer to equilibrate and are temperature sensitive.
The advantage of unsaturated salt standards is that they can be made to any water activity value, are faster to equilibrate and less temperature sensitive. The disadvantage of unsaturated standards is that they are single-use only and must be purchased as a consumable.
Conclusion
The availability of independent calibration standards of known value is one of the benefits of water activity testing that makes it more powerful than moisture content. Accuracy determination, defined as the agreement of a measured value with the true value, requires the existence of standards of known value. Consequently, since the water activity of salt standards is dictated and known through thermodynamics the accuracy of water activity instrumentation can be determined. The accuracy of a moisture content analyzer cannot be determined due to the lack of similar independent standards. Furthermore, the existence of 2 different types of standards, each with its own unique benefits, ultimately allows the user to choose the standard the best fits their needs. While providing a choice of standards seems beneficial, Novasina is the only water activity provider that provides both types of standards: saturated salt slurry standards called SAL-T and unsaturated salt solution standards called SAL-F. Contact Neutec Group to determine which water activity standard is best for you.